Table of Content
- Overview
- Scenario
- Further Analysis
- Immediate Actions – Phishing is Confirmed
- Analyzing Email header – Authentication
- Analyzing Email Header – Location
- Analysis using URLScan.io
- Sources
- Tools
Overview
Deloitte reported that 91% of all cyberattacks begin with a phishing email to an unsuspecting victim. Phishing attacks continue to be a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape, affecting both individuals and organizations worldwide.
Scenario
The user submitted a ticket reporting that their computer is behaving unusually, experiencing significant slowdowns, and generating unexpected data.
Note: This Analysis is solely focused on phishing email.
Initial Triage
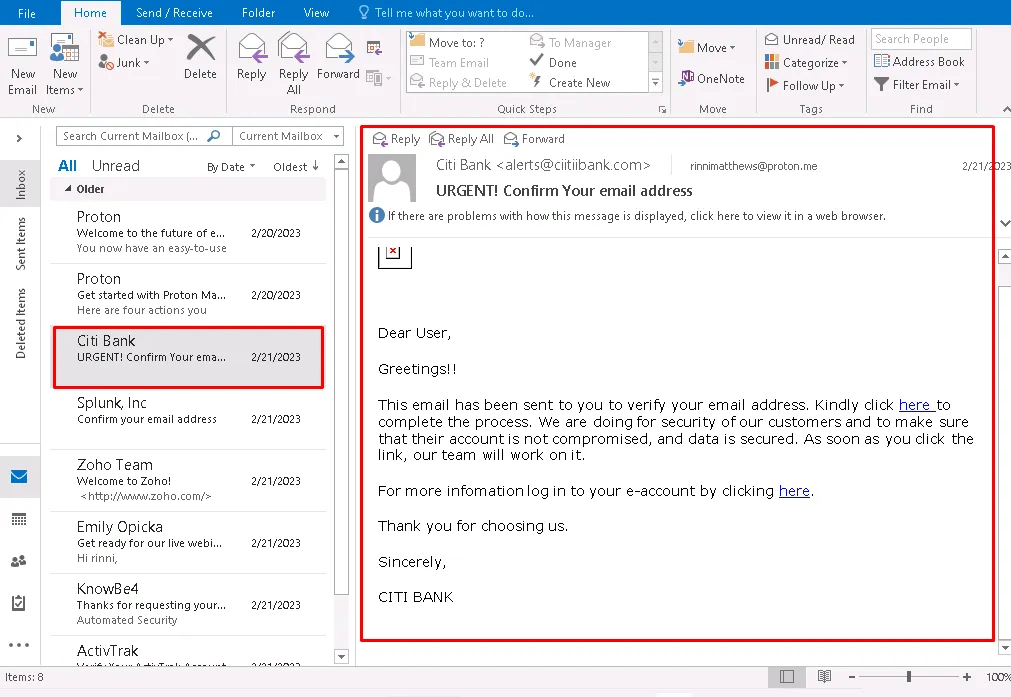
The user reported receiving an email claiming to be from Citi Bank, requesting email verification.
Analyzing Indicators
Looking at the there several red flags.
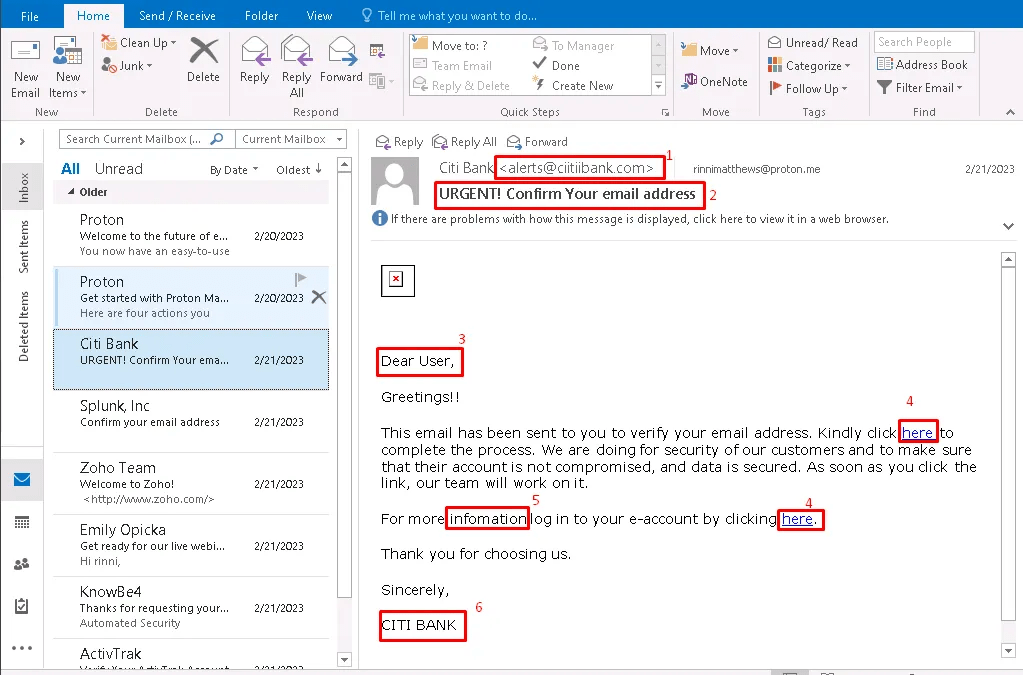
- Suspicious Sender Email Address
- The email claims to be from Citi Bank (alerts@citibank.com), but the real sender domain does not match Citi Bank’s official domain.
- Urgent & Alarming Subject Line
- “URGENT! Confirm Your email address” creates a sense of urgency, pressuring the recipient to act quickly without thinking.
- Generic Greeting (“Dear User”)
- Financial institutions always address customers by their full name. A vague greeting like “Dear User” suggests the email is not personalized and likely sent to multiple recipients.
- Suspicious Links (“here”)
- The email contains hyperlinks with vague anchor text (“here”), which is a common phishing tactic.
- Grammar and Formatting Issues
- “For more infomation log in to your e-account” → Missing punctuation and missing r in the information.
- Unofficial Email Signature
- (“CITI BANK”) Official email signature in communications does not look like “CITI BANK” in all caps.
Once phishing indicators are confirmed, checking further Indicator of Compromises (IOCs) such as:
- Task Manager to check for high CPU/memory usage.
- Check storage space (low disk space can cause slowness).
- Run a basic antivirus scan.
- Restart the system and check for improvements.
Further Analysis
Isolated the computer, installing Netcraft Extension on machine.
Clicking the hyperlink in the phishing email to copy its destination URL.

Confirmed the hyperlink is malicious
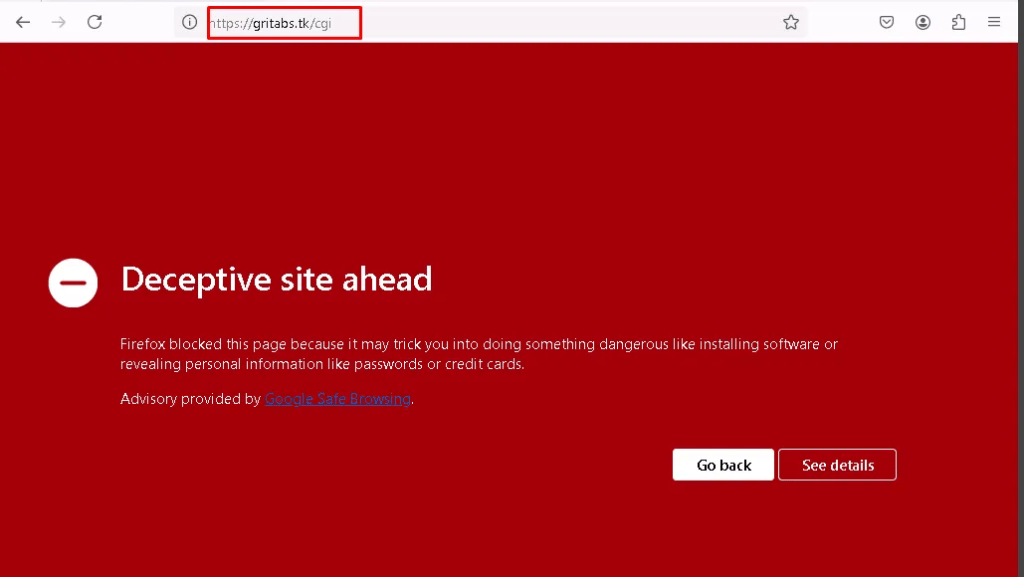
Analyzing the malicious link
Navigating to PhishTank makes it easy to submit a link and receive a detailed analysis.
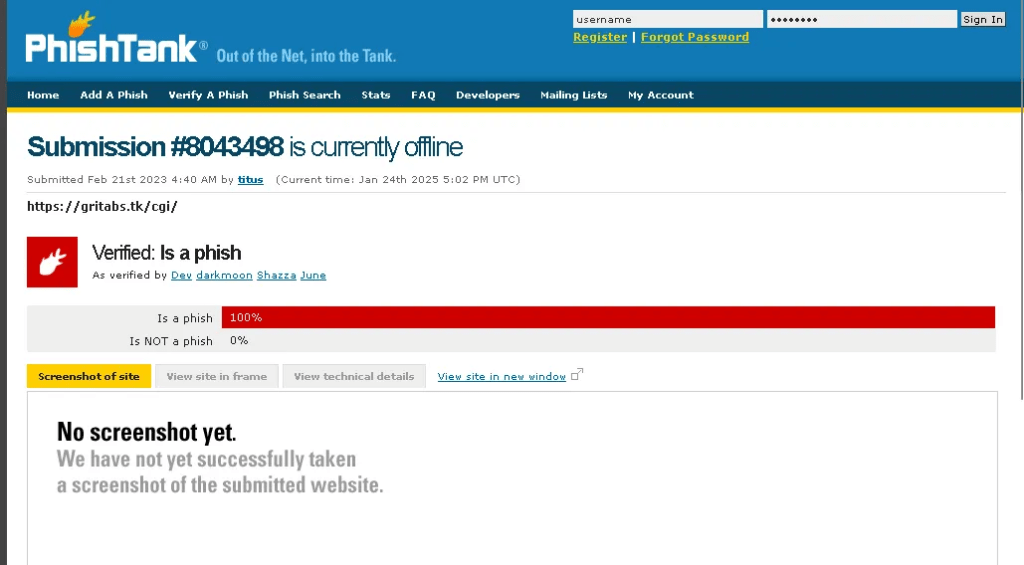
Verified, it is a phish
Immediate Actions – Phishing is Confirmed
- Immediately isolate the targeted system from the active network to prevent further compromise.
- Interview the users or complainants to gather details about the email incident, including their actions and the specifics of the attack.
- Ask the user whether they have downloaded any attachments, clicked on any links, or provided requested information, among other potential actions.
- Report the malicious links and IP addresses, then block them across servers, network devices, and all security solutions in place.
- Conduct behavioral analysis by safely opening the links in the email within a sandboxed environment to gather additional information on the attack.
Analyzing Email header – Authentication
An email header contains important information about the email, such as the sender, recipient, subject, and date. It also includes routing details, showing the path the email took from the sender to the recipient, and can reveal information about the servers involved in the delivery.
To access email header, Files>Properties>Message Option>InternetHeaders
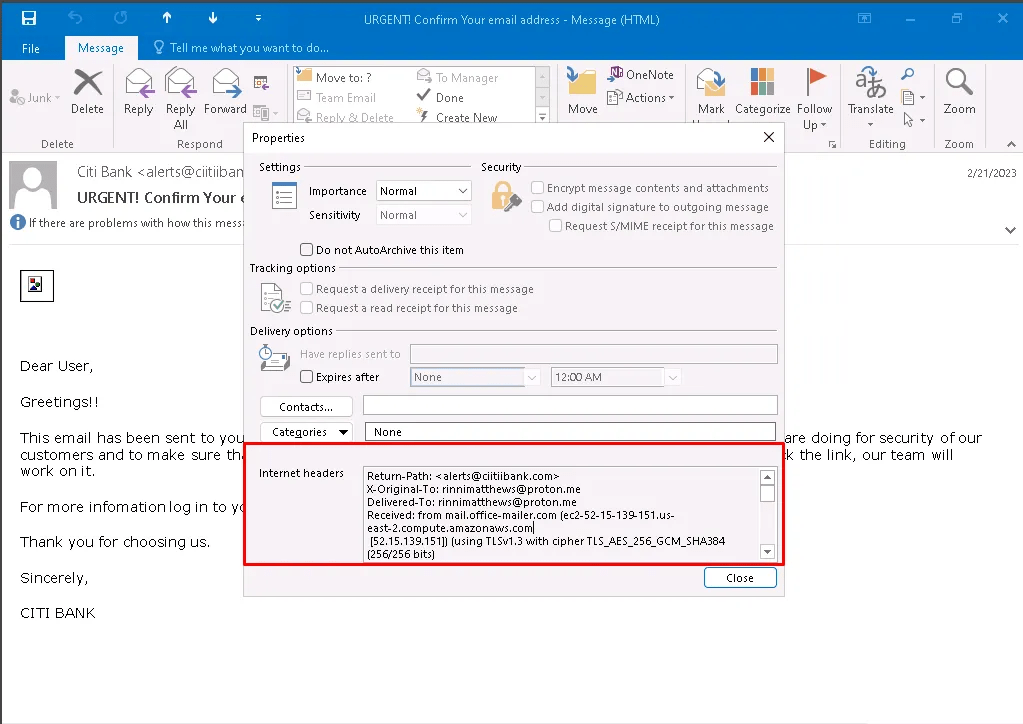
Copy the email header and paste it into MXToolbox for a detailed analysis.
After clicking “Analyze Header,” the results will be displayed. They show that SPF Alignment, SPF Authentication, DKIM Authentication, and DKIM Alignment are all marked as “Fail,” indicating that the email sender is likely illegitimate.
Each element is explained below:
- SPF Alignment verifies if the domain in the “From” address matches the domain used in the SPF record to check for authenticity.
- SPF Authentication checks whether the email’s sender IP is authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain in the SPF record.
- DKIM Authentication ensures the email’s integrity and authenticity by verifying the DKIM signature associated with the email.
- DKIM Alignment checks if the domain in the DKIM signature matches the domain in the “From” address, confirming consistency between the two.

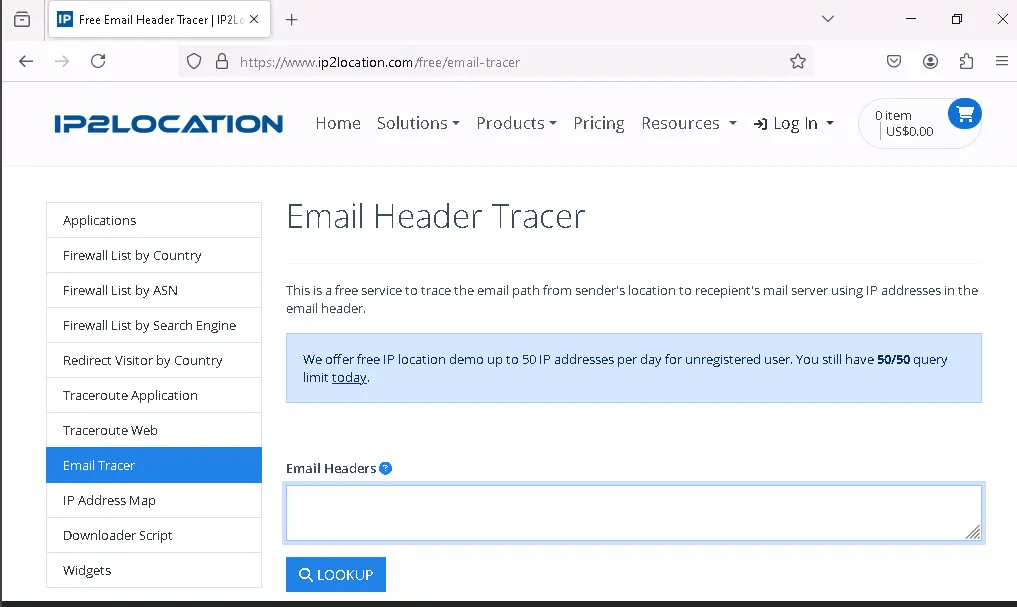
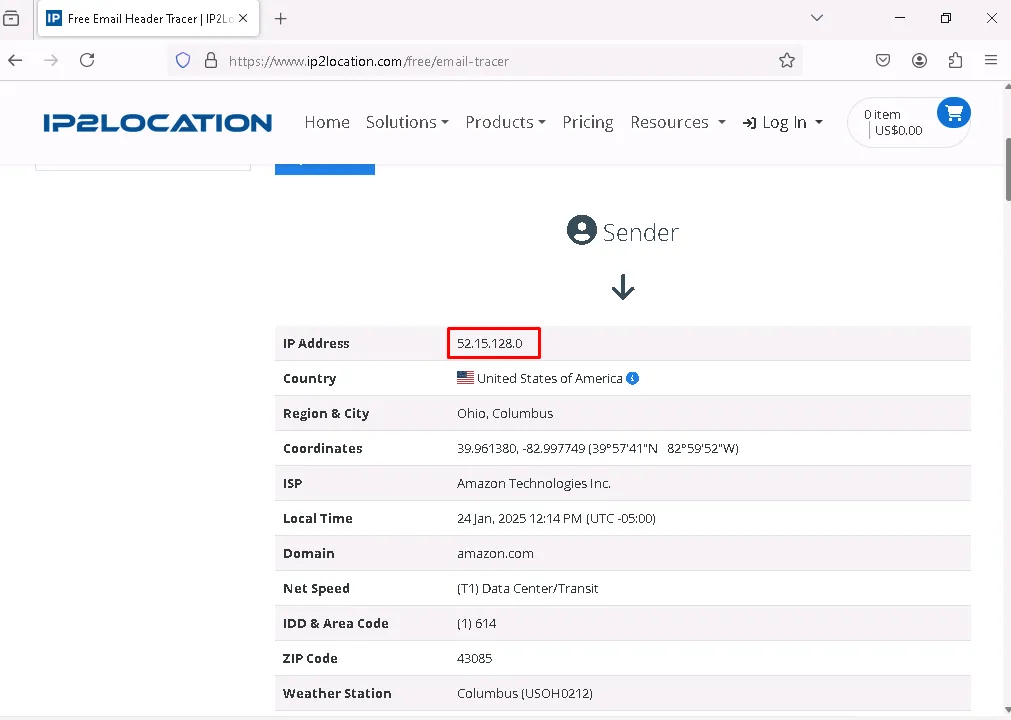
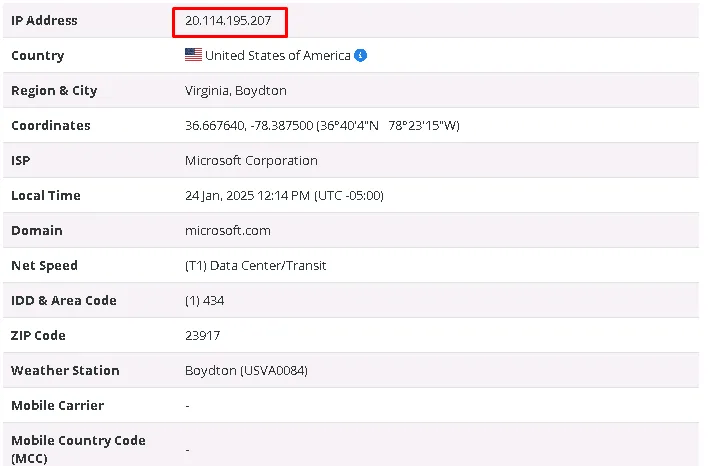
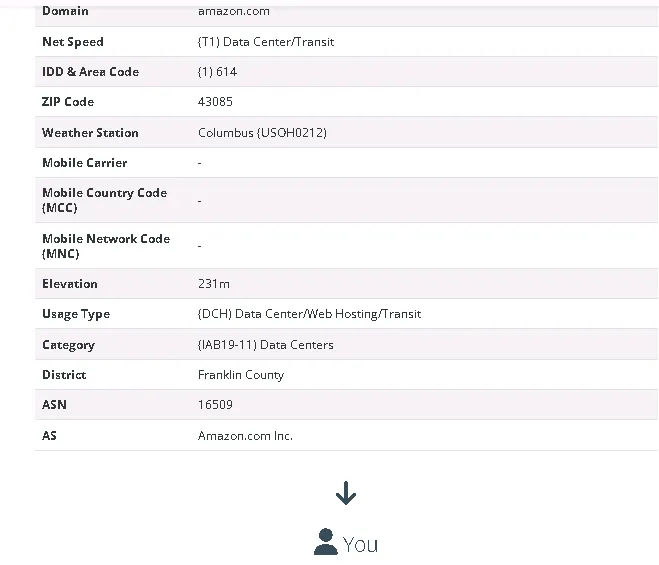
Analyzing Email Header – Location
This tool tracks the email’s journey from the sender to the recipient, providing detailed information such as the IP address, country, domain, zip code, and more.
Analysis using URLScan.io
URLScan.io is a free online tool that allows users to scan and analyze websites and URLs for potential security risks. It provides detailed information about the website’s behavior, structure, and any potential malicious activity, such as identifying suspicious links, embedded scripts, or domains.
Pasting the second hyperlink from the phishing email.


Sources
Branch, L. S. (2025, January 20). Consolidated federal laws of Canada, Canada evidence act. Canada Evidence Act. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/c-5/
Certified incident handler: ECIH. EC Council. (2025, January 15). https://iclass.eccouncil.org/our-courses/certified-incident-handler-ecih/
Tools
1- Netcraft: https://www.netcraft.com/apps-extensions/browser-extension/
2- PhishTank: https://phishtank.org/
3- MXToolbox: https://mxtoolbox.com/EmailHeaders.aspx
4- IP2Location: https://www.ip2location.com/free/email-tracer
URLScan: https://urlscan.io/

